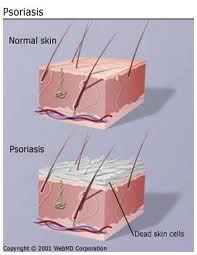
Psoriasis is an obstinate skin condition in which red patches of various sizes develop on the skin that are covered with dry, silvery scales. Psoriasis is a chronic skin disease that got its name from the Greek word meaning, “itch.”
In psoriasis the skin becomes inflamed and red eruptions appear on the surface of the skin that begin to itch excessively. These areas form thickened areas (plaques) that are covered with silvery scales over the reddened lesions. The skin at the joints may crack.
Location:
Psoriasis most often occurs on the elbows, knees, scalp, lower back, palms, and soles of the feet. However, no area of the skin is exempt, including the genital area. The disease may also affect the fingernails and toenails, and the soft tissues inside the mouth. About 15 percent of people with psoriasis have joint inflammation that produces arthritis symptoms. This condition is called psoriatic arthritis.
Psoriasis is categorized as mild, moderate, or severe, depending on the percentage of body surface involved and the impact on the patient’s quality of life.
Course of diseases:
The course of psoriasis is characterized by remissions and relapse. At some instances the patches disappear, just to appear after some period of time.
There are various factors ranging from climate, stress, infections and injuries that can trigger flare up of disease within short span of time even within few days. On the other hand there are certain other factors such as sunlight that significantly reduces the intensity of problem.
Impact on health: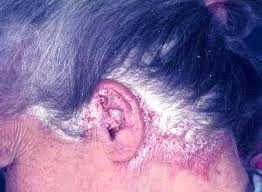
In some cases, psoriasis is so mild that it may go unnoticed. At the opposite extreme, there are victims having psoriatic patches almost everywhere on the body. People with psoriasis may suffer discomfort, including pain and itching, restricted motion in their joints, and emotional distress.
The unpleasant appearance of the patches, the chronic itching and flaking of psoriasis although is not life threatening, has definite impact on the self-esteem and life style of the psoriasis victim. Substantial time and money are spent trying to keep it under control.
Psoriasis > Symptoms and Types of psoriasis
Although psoriasis may affect any area of the body, it is most commonly found on the scalp, elbows, knees, hands, feet, and genitals.
Types of psoriasis
Psoriasis has many variants. The common ones are as follows:
- Plaque psoriasis is the most common type of the disease and is characterized by raised, thickened patches of red skin covered with silvery-white scales. Its scientific name is psoriasis vulgaris.
- Scalp psoriasis is a common variant of Psoriasis.
- Pustular psoriasis is characterized by pus-like blisters. Attacks of pustular psoriasis may be triggered by medications, infections, emotional stress, or exposure to certain chemicals. Pustular psoriasis may affect either small or large areas of the body.
- Erythrodermic psoriasis characterized by intense redness and swelling of a large part of the skin surface, is often accompanied by itching or pain. Erythrodermic psoriasis may be precipitated by severe sunburn, use of oral steroids (such as cortisone), or a drug-related rash.
- Guttate psoriasis is characterized by small, drop-like lesions on the trunk, limbs, and scalp. Guttate psoriasis is most often triggered by bacterial infections (for example, Streptococcus).
- Palmo-planter psoriasis is a common variant of Psoriasis affecting either the palms or soles or palms as well as soles. Palmo-plantar psoriasis is a chronic, recurring condition that affects the palms of hands and soles of feet.
- Inverse psoriasis is characterized by smooth red lesions in the folds of the skin like in the folds of the skin near the genitals, under the breasts, or in the armpits. Inverse psoriasis is related to increased sensitivity to friction and sweating and may be painful or itchy.
For the most part people with psoriasis can function normally. Sometimes people experience low self-esteem because psoriasis appears unsightly. Psoriasis is often misunderstood by the public, and this can make social interactions awkward. This may lead to emotional problems such as anxiety, anger, embarrassment, and depression.
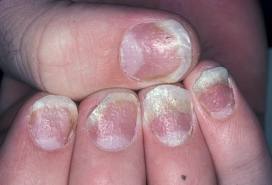
The Psoriatic Nail About 50 percent of persons with active psoriasis have psoriatic changes in fingernails and/or toenails. In some instances psoriasis may occur only in the nails and nowhere else on the body.
Psoriatic arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is all the more difficult situation where you find psoriasis associated with joint pain (arthritis). This shows deeper affection of the underlying problems. The changes in the blood which lead to psoriasis are now also bringing changes in the joints, which could even be irreversible. Any joint could be affected in this process. The joint affection relatively becomes more difficult to treat. Interestingly, there is good treatment for psoriatic arthritis in homeopathy, especially if treated in the early stages.
Homeopathic treatment for psoriasis: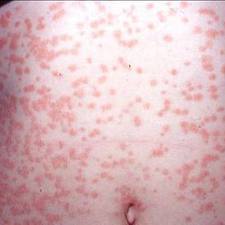
Psoriasis responds very well to homeopathy. The redness reduces, the itching reduces and the scaling reduces. The recurrence is brought under good control.
Homeopathy treats psoriasis by correcting internal immune imbalance, irrespective of the location of psoriasis. There are certain more commonly used medicines especially when psoriasis affects the scalp.
The scalp psoriasis may respond slower, in comparison to psoriasis on the skin.
If a patient has psoriasis on the skin and on the scalp, the skin form responds earlier, the scalp psoriasis responds later, however, that is not a rule.
Homeopathy does not suggest any use of cortisone based medication for scalp psoriasis.
Click on the links below to know more about management of psoriasis @ sattvam
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U0kTCzxVn8Y
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TBw7vorCLHc





