Anemia is the most common of all blood disorders. The term anemia (derived from Greek) means a deficiency of blood.
Anemia results from reduced red blood cell production in the bone marrow.
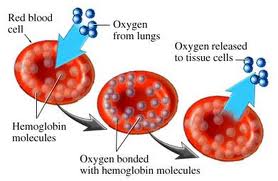
Hemoglobin is the oxygen carrying protein in blood. It is a major component of all red blood cells and gives them their red color. This protein picks up oxygen from the lungs, carries it throughout the body and delivers it to all your cells. In addition, hemoglobin also picks up some of the carbon dioxide produced by the cells and transports it to the lungs from where it is exhaled out.
Cells need oxygen for their basic functions and to keep them alive. Hence, without enough red blood cells to transport oxygen to your cells and carbon dioxide away from your cells, it is like literally suffocating every tissue and organ system in the body.
Symptoms of Nutritional anemia
Symptoms of anemia are usually very vague and hence, it goes undetected in many people. People tend to ignore these symptoms until they become quite disturbing. Thus, it is necessary to know some of the often ignored symptoms:
|
|
Must see your physician when:
- You feel tired for more than five days
- You are unable to perform routine activities
- There is persistent exhaustion with even minimal exertion
- The skin appears pale, and there is fatigue plus breathlessness on moderate exertion.
- Your tongue appears, smooth, shiny and very clean always
- There is yellowish (jaundiced) appearance of the skin.
- Your wounds don’t heal soon or when there is presence of bluish-green discolorations under the skin.
Some of the most common causes of nutritional anemia are:
- Iron deficiency
- Vitamin B12 Folic acid deficiencies (these usually occur together)
- Thyroid disorders
- Lead toxicities
- Infectious diseases like malaria
- Alcoholism
- Vitamin E and B6 deficiencies.
- Premature born infants.
- Medications which
- Prevent iron absorption from the gut e.g. ‘proton pump inhibitors’ in treating acidity, tetracycline etc.
- Cause chronic, mild bleeding from the gut e.g. NSAIDs (ibuprofen, naproxen used widely as pain-killers).
- Aspirin is another widely used medication known to cause mild to moderate bleeding from the gut.
- Hydrocortisones and valproic acid are drugs which cause folic acid deficiencies.
- Vitamin B12 deficiency can be caused by drugs like amoxicillin (antibiotic), and phenytoin (anti-convulsive).
Risk factors fro nutritional anemia:
Ones chances of developing anemia increase particularly if they are:
- Menstruating and having heavy bleeding or excessively long periods (monthly blood loss depletes iron)
- Pregnant
- Lactating
- Athletes (especially endurance athletes)
- An alcoholic
- Vegetarians or vegans
- Using nonprescription drugs and natural remedies whose side-effects are less known.
- Habituated to having tea in excess (tannin in tea causes decreased absorption of iron).
Homeopathic treatment for Nutritional anemia:
In addition to the supplements with iron and other components, homeopathic medications work wonders for cases of Nutritional anemia by treating the cause such as problems with absorption and assimilation of food. The medicines increase iron absorption and its assimilation. The medications act without any side-effects. Homeopathy is strongly suggested for Nutritional anemia.





