Irritable Bowel Syndrome
IBS is one of the most common disorders of digestive system producing a spectrum of symptoms such as persistent and recurring abdominal pain associated with passing of motion, change of bowel habit (diarrhea, constipation, or alternate diarrhea and constipation), etc. without any apparent cause. IBS is a syndrome because it can cause several symptoms in addition to those mentioned, like cramping, bloating, gas, frequent urge to pass stools, sensation of incomplete evacuation etc.

Effect on lifestyle
IBS can be nothing more than a mild annoyance, completely debilitating, or anywhere in between. Again, it depends on the person and how he or she reacts to it and treats it. IBS can, however, be very painful and can severely affect a person’s quality of life, and is second only to the common cold as a cause of absenteeism from work.
IBS and Stress
The key point is that IBS is strongly related to emotional stress and strain. Research on the psychosocial aspects of these disorders has yielded three general observations:
- Psychological stress exacerbates gastrointestinal symptoms.
- Psychological disturbances amplify illness experience and adversely affect health status.
- Having a functional GI disorder like IBS impairs the quality of one’s life.
Causes 
The factors that can adversely affect the job of the bowel are as follows:
- Psychological factors: Patients of IBS report of increasing symptoms during the events of stress and many patients with IBS report that their symptoms began during periods of major life stressors such as a divorce, death of a loved one, school exams, or after moving to a new job or city. About 50% patients exhibit range of emotional disturbance including anxiety, depression, and neurosis.
It is a known fact that our emotions and intestines are interwoven. The brain and the intestines are closely connected by nerve fibers that control the functioning of the intestines. It is believed that in IBS the communication between brain and gut may be impaired.
- . Sensitivity to food: Symptoms of IBS have also been known to be triggered by the ingestion of certain foods to which the individual is sensitive. Chocolate, milk products, caffeine, or large amounts of alcohol are frequent offenders.
One theory states that lack of fiber in the diet can have detrimental effect. This lack of fiber causes irregular contractions of the large intestines. - Genetics and heredity: Some studies indicate that there are more chances of IBS running in a family. It is believed that there are some inborn tendencies of an individual that make him/her react adversely to stress or certain food and resulting in IBS.
- Some patients develop IBS following an episode of gastroenteritis or abdominal surgeries like removal of gallbladder.
- Researchers have also found that women with IBS may have more symptoms during their menstrual periods, suggesting that reproductive hormones can increase IBS symptoms
- Conventional medicines: Many patients of IBS report worsening of their symptoms following use of some of the conventional medicines like antibiotics, steroids, anti-inflammatory medicines etc.
- Altered bowel movements/habits: Some people with IBS have constipation (difficult or infrequent bowel movements, hard stools); others have diarrhea (frequent loose stools, often with an urgent need to move the bowels); and some people experience both, for example several weeks of constipation followed by a few days of diarrhea. The diarrhea typically occurs immediately after a meal or when getting up in the morning. Sometimes people with IBS pass mucus with their bowel movements.
- Abdominal pain and cramps: The abdominal discomfort of an irritable bowel ranges from sharp, cramp to a continuous, dull ache. Common sites of pain include the lower abdomen, specifically the left lower quadrant. Meals may precipitate pain while pain is commonly relieved by defecation.
- Gas formation, bloating, abdominal distention: Patients frequently report increased amounts of bloating and gas and distended feeling.
- Urgency: Sometimes the person with IBS has a cramp and an urge to move the bowels but cannot do so.
- Sensation of incomplete evacuation: The patient feels like he still needs to have a bowel movement after he has already had one.(incomplete evacuation)
- Extra-colonial symptoms: In addition, a number of other symptoms not directly related to bowel may be present in patients with IBS. These include: nausea (with or without vomiting), feeling full after eating only a small meal, difficulty swallowing, a sensation of a lump in the throat or a closing of the throat, heartburn or acid indigestion, chest pain, sensation of urinary urgency, incomplete emptying after urinating, fatigue and generalized body ache or muscular pains, and pain during sexual intercourse.
Symptoms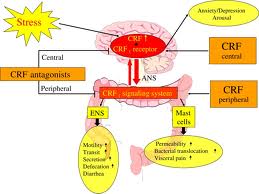
Although many IBS sufferers get similar symptoms, each individual with IBS has his own unique set of symptoms.
IBS presents in wide spectrum of severity. For some people it may just be an occasional mild episode or nuisance. For others, it can be a debilitating illness that causes frequent absenteeism from work.
The most common symptoms of IBS are as follows:
Homoeopathy effectively manages various symptoms of IBS gently and safely.





