Acne
Acne is a skin condition that causes pimples . This includes whiteheads, blackheads, and red, inflamed patches of skin (such as cysts).
Causes, incidence, and risk factors
Acne occurs when tiny holes on the surface of the skin become clogged. These holes are called pores.
- Each pore opens to a follicle. A follicle contains a hair and an oil gland. The oil released by the gland helps remove old skin cells and keeps your skin soft.
- When glands produce too much oil, the pores can become blocked. Dirt, bacteria, and cells build up. The blockage is called a plug or comedone.
- If the top of the plug is white, it is called a whitehead.
- If the top of the plug is dark, it is called a blackhead.
- If the plug breaks open, swelling and red bumps occur.
- Acne that is deep in your skin can cause hard, painful cysts. This is called cystic acne.
Acne is most common in teenagers, but anyone can get acne, even babies. Three out of four teenagers have some acne. Hormonal changes may cause the skin to be more oily.
Acne tends to run in families. It may be triggered by:
- Hormonal changes related to puberty, menstrual periods, pregnancy, birth control pills, or stress
- Greasy or oily cosmetic and hair products
- Certain drugs (such as steroids, testosterone, estrogen, and phenytoin)
- High levels of humidity and sweating
Eczema:
Atopic dermatitis is a long-term (chronic) skin disorder that involves scaly and itchy rashes.
Atopic dermatitis is due to a hypersensitivity reaction (similar to an allergy) in the skin, which leads to long-term swelling and redness (inflammation) of the skin. People with atopic dermititis may lack certain proteins in the skin, which leads to greater sensitivity.
Atopic dermatitis is most common in infants. It may start as early as age 2 to 6 months. Many people outgrow it by early adulthood.
People with atopic dermatitis often have asthma or seasonal allergies. There is often a family history of allergic conditions such as asthma, hay fever, or eczema. People with atopic dermatitis often test positive to allergy skin tests.
However, atopic dermatitis is not caused by allergies. The condition tends to get worse when the person is exposed to certain triggers.
The following can make atopic dermatitis symptoms worse:
- Allergies to pollen, mold, dust mites, or animals
- Cold and dry air in the winter
- Colds or the flu
- Contact with irritants and chemicals
- Contact with rough materials, such as wool
- Dry skin
- Emotions and stress
- Exposure to too much water, such as taking too many baths or showers and swimming too often
- Feeling too hot or too cold, as well as sudden temperature changes
- Fragrances or dyes added to skin lotions or soaps.
HOMOEOPATHY
Homeopathy has good scope in the treatment of acute, chronic and recurring eczema. The treatment is individual specific, that is, each case is evaluated as a different entity and the treatment in specific to the details of that particular case, tackling eczema from roots and helps in cure, safely and effectively.
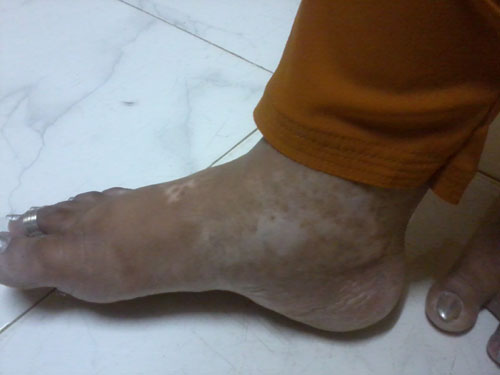
Leucoderma
Leucoderma is a skin condition in which there is a loss of brown pigment called Melanin,from areas of skin, resulting in irregular white patches that feel like normal skin.
Causes, incidence, and risk factors
Leucoderma appears to occur when immune cells destroy the cells that produce brown pigment (melanocytes). This destruction is thought to be due to an autoimmune problem, but the cause is unknown.
Leucoderma may appear at any age. There is an increased rate of the condition in some families. The condition affects about 1 out of every 100 people in the United States.
Leucoderma is associated with three other autoimmune diseases:
- Addison’s disease
- Hyperthyroidism
- Pernicious anemia
Symptoms
Flat areas of normal-feeling skin without any pigment appear suddenly or gradually. These areas have a darker border. The edges are well defined but irregular.
Leucoderma most often affects the face, elbows and knees, hands and feet, and genits. It affects both sides of the body equally.
Leucoderma is more noticeable in darker-skinned people because of the contrast of white patches against dark skin.
No other skin changes occur.
Homoeopathy promisingly helps Leucoderma as it tackles from the root,in a effective manner with no side effects.
Lichen planus
Lichen planus is a disease in which there is an itchy rash on the skin or in the mouth.
Causes, incidence, and risk factors
The exact cause of lichen planus is unknown. However, it is likely to be related to an allergic or immune reaction.
Risks include:
- Exposure to medications, dyes, and other chemical substances (including gold, antibiotics, arsenic, iodides, chloroquine, quinacrine, quinide, phenothiazines, and diuretics)
- Disorders such as hepatitis C
Lichen planus generally affects middle-aged adults. It is less common in children.
Symptoms
- Mouth lesions
- Tender or painful (mild cases may have no discomfort)
- Located on the sides of the tongue or the inside of the cheek
- Sometimes located on the gums
- Area of blue-white spots or “pimples”
- Lines of lesions that form a lacy-looking network
- Gradual increase in size of the affected area
- Lesions sometimes form painful ulcers
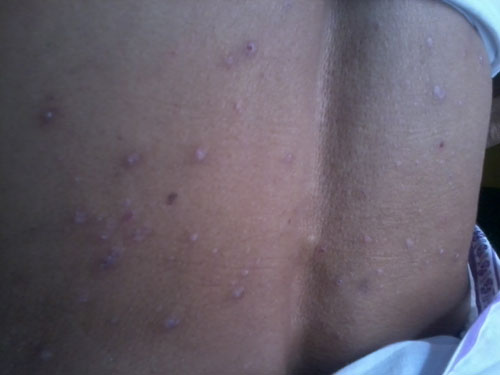
- Skin lesions:
- Usually located on the inner wrist, legs, torso, or genitals
- Itchy
- Even on both sides (symmetrical)
- Single lesion or clusters of lesions, often at sites of skin injury
- Papule 2 – 4 cm in size
- Papules clustered into a large, flat-topped lesion
- Lesions have distinct, sharp borders
- Possibly covered with fine white streaks or scratch marks called Wickham’s striae
- Shiny or scaly appearance
- Dark colored — reddish-purple (skin) or gray-white (mouth)
- Possibility of developing blisters or ulcers
Other symptoms include:
- Dry mouth
- Hair loss
- Metallic taste in the mouth
- Ridges in the nails (nail abnormalities)
Psoriasis:
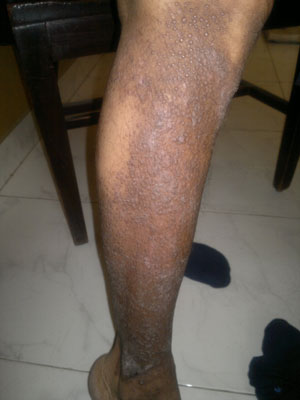
- Psoriasis is a common skin condition that causes skin redness and
irritation. Most people with psoriasis have thick, red skin with flaky,
silver-white patches called scales.
- Symptoms include:
- Irritated, red, flaky patches of skin
- Most often seen on the elbows, knees, and middle of the body
- Red patches may appear anywhere on the body, including the scalp
- The skin may be:
- Itchy
- Dry and covered with silver, flaky skin (scales)
- Pink-red in color (like the color of salmon)
- Raised and thick
- Causes, incidence, and risk factors
- Psoriasis is very common. Anyone can get it, but it most commonly
begins between ages 15 and 35.
- It is not contagious. You cannot spread it to others.
- Psoriasis seems to be passed down through families. Doctors think it
probably occurs when the body’s immune system mistakes healthy
cells for dangerous substances. See also: Inflammatory response
- Usually, skin cells grow deep in the skin and rise to the surface about
once a month. In persons with psoriasis, this process is too fast. Dead skin cells build up on the skin’s surface.
- The following may trigger an attack of psoriasis or make the condition
more difficult to treat:
- Bacteria or viral infections, including strep throat and upper respiratory
infections
- Dry air or dry skin
- Injury to the skin, including cuts, burns, and insect bites
- Some medicines, including antimalaria drugs, beta-blockers, & lithium
- Stress
- Too little sunlight
- Too much sunlight (sunburn)
- Too much alcohol
Skin allergy or Urticaria
- Hives are raised, often itchy, red welts on the surface of the skin. They are usually an allergic reaction to food or medicine.
- Causes, incidence, and risk factors
- When you have an allergic reaction to a substance, your body releases histamine and other chemicals into your bloodstream. This causes itching, swelling, and other symptoms. Hives are a common reaction, especially in people with other allergies such as hay fever.
- When swelling or welts occur around the face, especially the lips and eyes, it is called angioedema. Swelling from angioedema can also occur around your hands, feet, and throat.
- Many substances can trigger hives, including:
- Animal dander (especially cats)
- Insect bites
- Medications
- Pollen
- Shellfish, fish, nuts, eggs, milk, and other foods
- Hives may also develop as a result of:
- Emotional stress
- Extreme cold or sun exposure
- Excessive perspiration
- Illness (including lupus, other autoimmune diseases, and leukemia
- Infections such as mononucleosis
- Symptoms
- Itching
- Swelling of the surface of the skin into red- or skin-colored welts (called wheals) with clearly defined edges
- The hives may get bigger, spread, and join together to form larger areas of flat, raised skin.
- Complications
- Anaphylaxis (a life-threatening, whole-body allergic reaction that causes breathing difficulty)
- Swelling in the throat can lead to life-threatening airway blockage
- Homoeopathy is safe and curative in treatment of urticaria
check video here
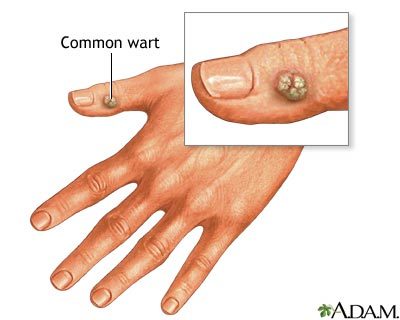
Warts
Warts are small, usually painless growths on the skin caused by a virus called human papillomavirus (HPV). Most, but not all, are generally harmless.
- Warts can be disfiguring and embarrassing. Sometimes they itch or hurt (particularly on the feet). Some warts spread through sexual contact.
- Different types of warts include:
- Common warts usually appear on the hands, but can appear anywhere. They usually do not cause pain unless they are repeated rubbed against.
- Flat warts are generally found on the face and forehead. They are common in children, less common in teens, and rare in adults.
- Genital warts(condyloma) are usually found on the genitals, in the pubic area, and in the area between the thighs, but they can also appear inside the vagina and anal canal.
- Plantar warts are found on the soles of the feet. They can be very painful. Many of them on the foot may cause difficulty walking or running.
- Subungual and periungual warts appear under and around the fingernails or toenails.
check video here





