Schizophrenia, also sometimes called split personality disorder, is one of the psychotic mental disorders and is characterized by symptoms of thought, behavior, and social problems.
Schizophrenia seems to result from a breakdown in the mental process by which we differentiate our inner self from the outside world. To a normal person, thinking, speaking and hearing are quite different subjective experiences, but in schizophrenia, this differentiation becomes blurred.

Symptoms Schizophrenia:
- Disturbance in thinking :
The thought problems associated with schizophrenia are described as irrelevant, in that the person’s thinking is completely out of touch with reality at times. Patient experience his thought being control by an external force.
- Disturbance of verbal behavior :
The patient gives new meaning to words or coining new words, repeating words used in interview’s question, senseless repetition of words or phrases, linking of words without meaning.
- Disturbance of motor behavior:
The individual who is schizophrenic having the following complaints which are usually observed by relatives and by himself for example stereotyped behavior, destructive behavior, criminal behavior , withdrawal behavior, excessive day dreaming.
- Disturbance of perception :
The sufferer may hear voices or see people that are in no way present or feel like bugs are crawling on their skin when there are none.
- Disturbance of emotions:
The patient has diminished intensity of emotional experience, inability to experience or imagine pleasant emotions, loss of empathy and simultaneous experiencing of two opposite types of feelings.
- Genetics and hereditary.
- Personality type.
- Social factors.
- Difficult circumstances like early loss of parent, parental poverty, bullying, witnessing parental violence, emotional, sexual or physical abuse, physical or emotional neglect etc.
- It may work in early and mild cases
- It is based on deeper understanding of the patients mind set, his stress coping system and genetic tendency.
- It is free from side effects.
- It is not habit forming.
- It does not lead to drug dependency.
Causes of Schizophrenia :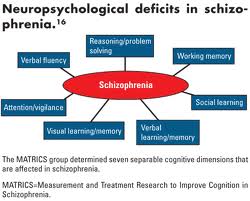
There is more than one reason why patients developed schizophrenia. Researchers and scientist are trying to find out more about biological, psychological and social factors which influence the development of schizophrenia. The following are all believed to play role in the occurrence of schizophrenia.
|
Sr No |
Types of schizophrenia |
Description |
| 1. | Paranoid schizophrenia | Preoccupied with one or more visual or hearing delusions e.g. Someone following him or some body is plotting plan to harm him. |
| 2. | Disorganized schizophrenia | Irrelevant speech and behavior. |
| 3. | Catatonic schizophrenia | The person with this type of schizophrenia has stereotyped behavior, imitation of movements or gesture, withdrawn behavior and repeating what others say or do. |
| 4. | Undifferentiated schizophrenia | This is characterized by episodes of delusions (false belief or opinion), hallucinations (the object or event so perceived), irrelevant speech or behavior, negative symptoms (destructive behavior). |
| 5. | Residual schizophrenia | This kind of schizophrenia having social withdrawal, eccentric behavior, illogical thinking etc. |
Homeopathy for Schizophrenia:
It may be noted that homeopathy does not work effectively in all cases of Schizophrenia, especially those that are chronic, severe and having drug-dependency. Homeopathy is not recommended in Schizophrenia, in our experience.





