Acromegaly is a hormonal disorder, due to excess secretion of growth hormone (GH) and occurs in middle-aged adults. This hormone in normally secreted by the ‘Pituitary’, a gland situated deep within the brain. Whenever there is increased secretion of GH, the clinical condition is called acromegaly (meaning enlarged extremities).
A similar excess occurring if occurring in childhood causes the condition ‘gigantism’.
Acromegaly is uncommon (3-4 per 100000 people). Physical changes occur so gradually that it is easy to miss the disease altogether in the initial stages.
Few initial (early) symptoms: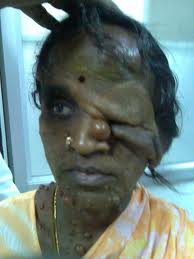
- Enlarged hands and feet.
- Shoes do not fit, rings on fingers become tight.
- Changes in facial features
- Protrusion of lower jaw
- Enlarged nose
- Thickened lips
- Teeth show wider spacing.
Signs & symptoms seen as the disorder progresses:
- Coarse, oily, thickened skin
- Excessive sweating and body odor
- Small outgrowths of skin tissue (skin tags)
- Fatigue and muscle weakness
- A deepened, husky voice due to enlarged vocal cords and sinuses
- Severe snoring due to obstruction of the upper airway
- Impaired vision
- Headaches
- Enlarged tongue
- Pain and limited joint mobility
- Menstrual cycle irregularities in women
- Erectile dysfunction in men
- Enlarged liver, heart, kidneys, spleen and other organs
- Increased chest size (barrel chest)
Causes: 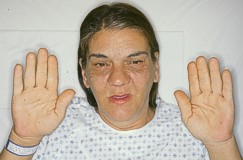
The most common cause of acromegaly is a tumor. These tumors can be of two types:
Pituitary tumors: These tumors are almost always non-cancerous and benign, called ‘adenomas’
This tumor secrets excess amounts of growth hormone which causes most of the symptoms.
Some symptoms like impaired vision and headaches are caused due to the tumor growing in size and pressing on nearby brain tissues.
Non-Pituitary tumors: Tumors present elsewhere in the body (pancreas, lungs, and adrenal glands) begin to secrete growth hormone resulting in excess hormone circulation.
Diagnosis
The progress of the disease being very slow, it is easy to miss acromegaly. Even with friends and family members, the condition can go unnoticed as changes are very subtle.
1) Growth Hormone suppression test.
GH levels in the blood are measured before and after having a fixed amount of glucose orally. If the GH levels after having glucose fail to fall, the diagnosis of acromegaly is made.
2) GH & IGF-I measurements.
Elevated levels of these hormones in spite of fasting overnight, is indicative of acromegaly.
3) Imaging.
CT and MRI scans can pinpoint the locations of pituitary as well as non-pituitary tumors.
Sequelae:
Acromegaly is either a cause of or associated along with the following conditions outlined below:
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure.
- Other cardio-vascular diseases (enlargement of the heart muscles ‘ myopathies)
- Osteoarthritis
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Sleep apnea syndrome
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Reduced secretion of other pituitary hormones (panhypopituitarism)
- Spinal cord compression
- Loss of vision
- Formation of pre-cancerous growths (polyps) within the intestine (colon).
- Benign tumors (fibroids) within the uterus.
Treatment
More than one form of treatment is usually required. Both medications and surgery are usually indicated, the aim being to reduce the total amount of GH in circulation.
Homeopathic Treatment :
Homeopathy system does not have significant treatment for Acromegaly. However, homeopathy can successfully treat some of the end results of the disease process helping to balance GH in circulation.





